The Landscape
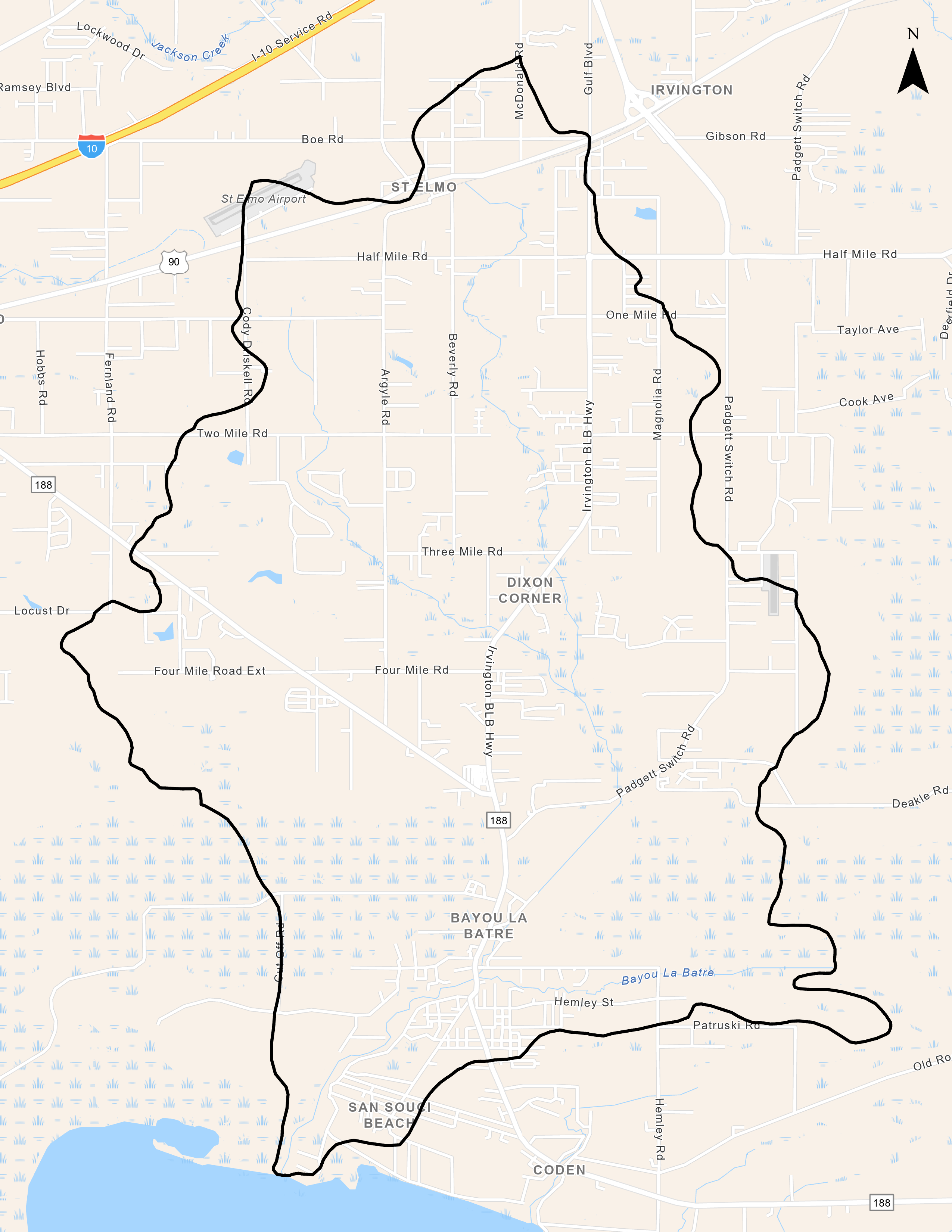
Watershed Size and Location
The Bayou LaBatre Watershed covers over 19,500 acres in south Mobile County and flows southwesterly into Portersville Bay and Mississippi Sound. The City of Bayou LaBatre, which is located within the watershed, is the source of the urban component of the watershed. Total land use breakdown: 13% urban, 32% agricultural land, 51% forested, 2% water/wetlands.
Main Tributaries and Tidal Influence
Bayou La Batre (HUC 031700090102) is a shallow tidally-influenced river that receives drainage from several named tributaries (Hammar Creek, Bishop Manor Creek, and Carls Creek) and multiple unnamed tributaries which all flow south into the bayou. Bayou La Batre, Carls Creek, and several unnamed tributaries are all tidally influenced.
Water Use Classification and Impairments
ADEM's water use classification for Bayou La Batre is Fish & Wildlife. Bayou La Batre was originally placed on the State's 303(d) list for pathogens in 1998 with a TMDL developed in 2009. According to a sub-estuary monitoring report by ADEM based on National Coastal Assessment water quality index, the lower half of the Bayou la Batre sub-estuary is rated “Fair” while the upper half is rated “Poor”. There are no NPDES discharges within the watershed, and nonpoint sources appear to be a significant source of pathogen contamination, with the TMDL indicating sanitary sewer overflows and agriculture runoff being the probable sources.
Human Uses
The City of Bayou La Batre has been developed as a commercial coastal fishing and shipbuilding community, and the water-front primarily consists of privately owned and operated seafood processing plants, commercial offloading docks, shipyards, and marinas. The only public access available is via the Bayou La Batre boat launch. The adjacent nearshore waters of Portersville Bay are important areas for commercial and recreational fishing (including shellfish harvesting) and support multiple commercial oyster aquaculture operations.
Ecological Importance
Large areas of pine Flatwoods and maritime forest habitat dominate the natural cover within the watershed and provide habitat for an array of reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals. USFWS documented T&E Species: Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris), Gulf sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi) Kemp's Ridley sea turtle (Lepidochelys kempii) and the Loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta). State protected species include the Mississippi diamondback terrapin (Malaclemys terrapin pileata) and alligator snapping turtle (Macroclemys temmincki).




